Definition: Supply and demand are economic are the economic forces of the free market that control what suppliers are willing to produce and what consumers are willing and able to purchase.
What Does Supply and Demand Mean?
Contents [show]
What is the definition of supply and demand? The term supply refers to how much of a certain product, item, commodity, or service suppliers are willing to make available at a particular price. Demand refers to how much of that product, item, commodity, or service consumers are willing and able to purchase at a particular price.
In other words, supply pertains to how much the producers of a product or service are willing to produce and can provide to the market with limited amount of resources available. Whereas, demand is how much of that product or service the buyers desire to have from the market.
Law of Supply and Demand
Demand and supply play a key role in setting price of a particular product in the market economy. Since demands of buyers are endless, not all that is demanded can be supplied due to scarcity of resources. This is where the relationship of demand and supply plays a significant role, allowing efficient allocation of resources and determining a market price for the product or service, known as equilibrium price. This price reflects the price at which suppliers are willing to supply and the buyers are willing to buy from the market.
The mechanism of determining market price through demand and supply can be better understood by observing the market economic theories.
Supply and Demand Curve Example
According to the law of demand, as the price of a product or service rises, the demand of buyers will decrease for it due to limited amount of cash they have to make purchases.
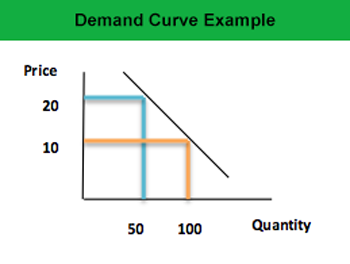
Example 1: A shopkeeper was offering a box of chocolate at price of $20, for which he was able to sell on average 50 boxes every week. He decided to offer 50% discount, decreasing the price to $10. This resulted in increase of his sales to 100 boxes each week.
According to the law of supply, as the price of a product increases, the suppliers will be more willing to supply that product as they can enjoy higher profits by selling that product or service.
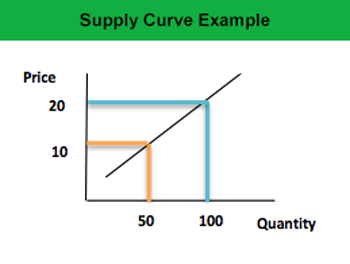
Example 2: A factory worker is paid $10 for providing his services to the factory for 50 hours per day. However, due to extra workload, more services were required per day for which the worker would only provide 100 hours if he were paid more i.e. $20.
From this we can conclude that demand has an inverse relationship with price; whereas, supply has a direct relationship with price. Therefore, when both demand and supply are put together, we can determine the equilibrium price, which is the market price of a product or service. This is the point at which the quantity supplied and quantity demanded is exactly equal and the resources are efficiently allocated.
Supply and Demand Graph
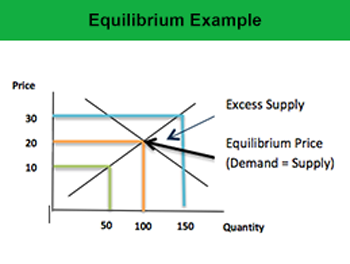
Example 3: Jack initiated a hot dog selling business and decided to sell 150 hot dogs per week, pricing each at $30. Other hot dog sellers in the market had been selling hot dogs for $20, which diverted the potential customers away. Jack was left with excess supply of hot dogs with no buyers willing to purchase at price $30.
Example 4: Jennifer offered to pay $10 to the shopkeeper for a CD she wanted to buy. The shopkeeper denied arguing that the costs he incurs to produce one CD are $12 and he will be left with nothing but a loss of $2. So the shopkeeper was only ready to accept minimum of $20 for each CD, which is the market rate.
Summary Definition
Define Supply and Demand: Supply & Demand means the amount of goods or services companies are willing to produce and the amount of goods or services that consumers are willing to purchase.


