 Definition: Accounting standards are rules and guidelines set up by governing bodies, like FASB and IASB, to keep accounting practices consistent and understandable across all companies and industries.
Definition: Accounting standards are rules and guidelines set up by governing bodies, like FASB and IASB, to keep accounting practices consistent and understandable across all companies and industries.
What Does Accounting Standards Mean?
Contents
- What Does Accounting Standards Mean?
- Example
- The Role of Governing Bodies
- The Importance of Accounting Standards
- Key Accounting Standards and Their Applications
- Challenges in Implementing Accounting Standards
- Technology and the Future of Accounting Standards
- Real-World Example: Applying Standards to Revenue Recognition
- Benefits of Converging Accounting Standards
- Summary Definition
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Bottom Line
What is the definition of accounting standards?
Accounting standards form the backbone of financial reporting, establishing a unified framework for recording and presenting financial information. These rules ensure consistency, transparency, and reliability across industries and geographies, enabling stakeholders to make informed decisions.
By promoting uniformity, accounting standards enhance the comparability of financial statements, fostering trust in financial markets and contributing to global economic stability.
These rules have an impact both on a national economy and on the economic and fiscal policy. With the implementation of accounting guidelines on a national scale, countries are able to implement a common terminology in the economic world and perform a precise, uniform, objective and correct calculation of data on the financial position and results of business units.
The International Accounting Standards (IAS) constitute a single set of high-quality accounting standards, which help in the preparation of consolidated financial statements, including the balance sheet, income statement, statement of changes in the financial position, cash flow statement and explanatory notes.
The standardization of the accounting procedures helps businesses to record and monitor their business activity and achieve comparability of accounting information between companies that operate in the same industry. By applying the same accounting principles and methods, businesses ensure homogeneous, reliable and accurate data and information about their assets, liabilities, financial position, and overall activity.
Let’s look at an example.
Example
Company ABC has bought a second plant for $400,000. In the purchase contract, it is stated that the value of the land is $100,000, and the value of the building is $300,000. Also, the company pays notary fees amounting to $10,000. In addition, Company ABC leases a new machinery for $120,000 and duration of 4 years. The annual rent amounts to $30,000. The initial value of transport is $100,000.
Roger, the company’s accountant needs to record these transactions, using the international accounting guidelines, as follows:
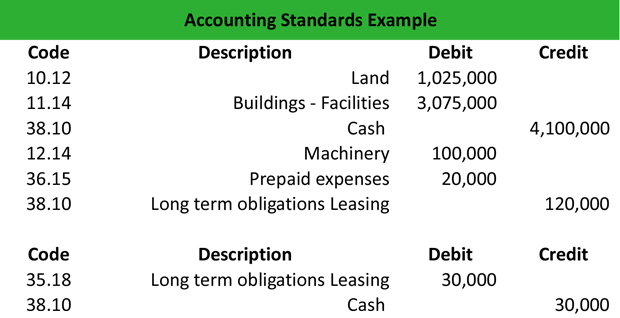
Once the company signs the lease contract, Roger will make the bottom entry.
Then, he calculates the depreciation of the machinery for the first year, using the straight-line method.
Useful life of the machinery: 4 years
Acquisition cost = $100,000
Annual depreciation = Acquisition cost / useful life = $100,000 / 4 = $25,000.
The Role of Governing Bodies
The development and implementation of accounting standards are overseen by governing bodies like the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) in the United States and the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) globally.
FASB sets the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP), which govern accounting practices in the U.S.
IASB issues the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), a set of globally recognized standards adopted by over 140 countries.
These organizations work collaboratively to address the needs of diverse stakeholders, including investors, regulators, and business managers, ensuring that financial information remains relevant and reliable.
The Importance of Accounting Standards
Accounting standards serve several critical purposes:
Consistency
By defining rules for recording and reporting transactions, standards ensure uniformity across companies and industries. For example, two companies in the same industry applying the same depreciation method can produce comparable financial statements.
Transparency
Standards provide a clear framework for disclosing financial information, reducing the risk of misrepresentation or fraud.
Investor Confidence
Reliable and standardized financial reporting builds trust among investors, facilitating capital allocation and economic growth.
Global Integration
As businesses increasingly operate across borders, international standards like IFRS enable seamless financial communication and collaboration.
Key Accounting Standards and Their Applications
GAAP and IFRS represent two primary sets of accounting standards, each with unique principles and applications.
GAAP: Emphasizes detailed rules and guidelines, offering a structured approach to financial reporting. It is widely used in the U.S. for regulatory compliance and investor communication.
IFRS: Adopts a principle-based approach, focusing on broader guidelines that allow for flexibility in interpretation. This makes IFRS more adaptable to diverse business environments.
For instance, while GAAP mandates the use of the last-in, first-out (LIFO) inventory valuation method, IFRS prohibits it. Such differences highlight the need for businesses operating internationally to understand and reconcile varying standards.
Challenges in Implementing Accounting Standards
Despite their benefits, the adoption and enforcement of accounting standards can present challenges:
Global Variability: Differences between GAAP and IFRS create complexity for multinational companies required to comply with both standards.
Industry-Specific Needs: Certain industries, such as banking or insurance, require tailored standards that address their unique financial structures.
Cost of Compliance: Implementing new or updated standards often involves significant costs, including training, system upgrades, and process changes.
For example, when IFRS 16 was introduced to standardize lease accounting, many companies faced challenges in transitioning to the new requirements, particularly those with extensive lease portfolios.
Technology and the Future of Accounting Standards
Advancements in technology are reshaping how accounting standards are applied and enforced. Automation, artificial intelligence (AI), and blockchain are enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of financial reporting:
- Automation: Software solutions like SAP and Oracle streamline compliance by embedding accounting standards into financial systems.
- AI: AI-powered tools analyze vast datasets to ensure compliance and detect discrepancies, reducing the risk of errors.
- Blockchain: Blockchain technology creates immutable records of transactions, ensuring transparency and accountability in financial reporting.
For instance, a company using blockchain to record its supply chain transactions can demonstrate compliance with inventory accounting standards while providing stakeholders with real-time insights.
Real-World Example: Applying Standards to Revenue Recognition
Revenue recognition is a critical area governed by accounting standards. Under IFRS 15 and ASC 606 (GAAP equivalent), revenue is recognized when control of goods or services is transferred to the customer, not necessarily when payment is received.
Consider a software company offering subscription-based services. According to the standards, revenue must be recognized monthly as the service is provided, even if the customer pays the full amount upfront. This ensures that financial statements accurately reflect the company’s performance over time.
Benefits of Converging Accounting Standards
Efforts to harmonize GAAP and IFRS aim to reduce global variability, making it easier for companies to operate internationally. Convergence initiatives focus on aligning key principles, such as lease accounting, financial instruments, and revenue recognition.
For example, the joint development of the revenue recognition standard by FASB and IASB marked a significant step toward creating a unified framework, simplifying reporting for multinational corporations.
Summary Definition
Define Accounting Standards: Accounting standard means a rule or guideline for how financial activities are recorded and reported to third parties.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are accounting standards?
Accounting standards are a set of rules and guidelines that govern how financial transactions are recorded and reported. They ensure consistency, transparency, and comparability across financial statements.
Why are accounting standards important?
Accounting standards ensure that financial information is reliable and comparable, allowing stakeholders to make informed decisions. They also promote transparency and build trust in financial reporting.
What is the difference between GAAP and IFRS?
GAAP is a detailed rule-based standard primarily used in the U.S., while IFRS is a principle-based standard used internationally. Both frameworks aim to ensure accurate and transparent financial reporting but differ in application and flexibility.
How do accounting standards impact businesses?
Accounting standards guide businesses in recording and presenting financial data accurately, helping them comply with regulations and attract investors. They also simplify comparisons with competitors and ensure financial transparency.
Bottom Line
Accounting standards are essential for maintaining the integrity and comparability of financial reporting. By providing a consistent framework for recording and presenting financial information, these standards enable stakeholders to make informed decisions, fostering trust and stability in financial markets.
While challenges such as global variability and compliance costs remain, the continued evolution of accounting standards, supported by technological advancements, promises a more integrated and transparent financial future. Businesses that understand and effectively apply these standards position themselves for success in an increasingly complex and interconnected world.


